cfTrack: A Method of Exome-Wide Mutation Analysis of Cell-free DNA to Simultaneously Monitor the Full Spectrum of Cancer Treatment Outcomes Including MRD, Recurrence, and Evolution
2022, Clinical Cancer Research
Xianghong Jasmine Zhou Group
Longitudinal 하게 tissue 를 채취하는 것이 어렵기 때문에, liquid-biopsy 가 각광을 받고 있음.
하지만 이전의 liquid-biopsy 접근들은 cfDNA 안의 low tumor fraction 을 잡아내기 위해서 deep sequencing 기반의 small panel (tumor-informed) 에 의존하는데, 한계가 존재함
- Deep sequencing 의 비용 문제로 인해 적은 수의 mutation 만을 track 할수 없음 / 혹은 알려진 mutation 만 추적가능.
- 실험적 design 이 어려움.
- Emerging mutation 의 검출이 어려움. ( 실제로 secondary cancer 의 30% 는 de nove mutation 에 의해서 생겨남)
- LoD 를 noncancer individual 로 잡아서, 개인간 / 실험간 차이가 있을 수 있음.
최근에 WGS 기반의 연구들도 진행되었지만, 이러한 한계점에 대한 설명을 포함하고 있지는 않음.
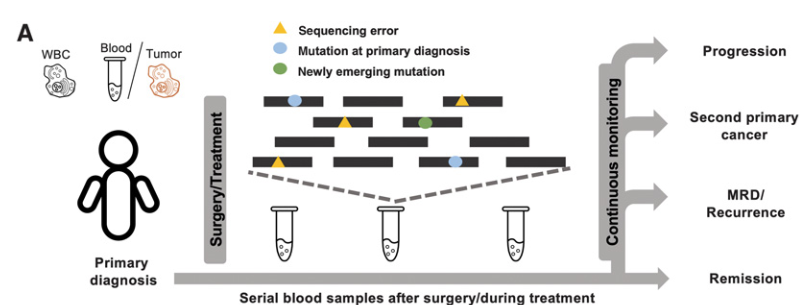
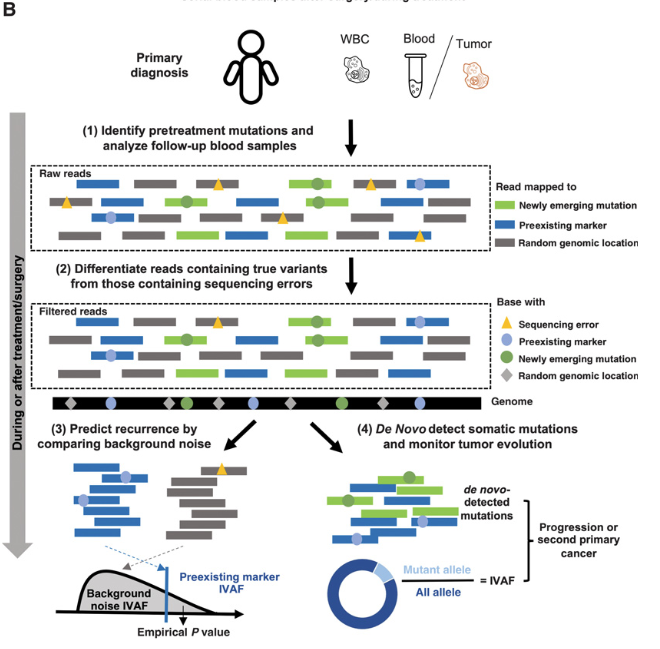
이 논문에서는 cfDNA Whole-Exome sequencing ( WES ) 기반의 기술을 소개함. 기존에 존재하던 mutation 뿐만 아니라, emerging mutation 이나 tumor progression, secondary cancer 도 검출이 가능함.
- Pre-treatement sample 사용 ( tumor or blood )
- Sample-specific background error correction
Tumor evolution 의 monitor 를 위해서는
- Post-treatment blood sample 이용
- 이전 기술인 cfSNV 사용함.
Methods
Personalized cancer monitoring
1) Pre-treatment samples
- 기존에 존재하는 mutation 을 찾기 위해서 pre-treatement sample 에서 plasma/tumor + matched WBC 를 사용
- low tumor fraction 으로 인해 존재하는 모든 cloncal mutation 을 가져감 ( VAF 가 높은 것들 위주로 선택 )
- 100~200x sequencing 은 low tumor fraction 으로 인해 cfDNA 에서 특정 locus 를 support 하는 read 의 수가 적을 수 있으므로, clonal mutation 을 suport 하는 모든 read 들을 모음.
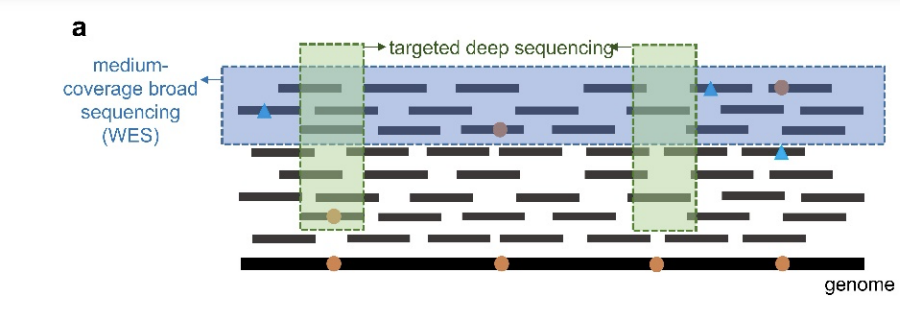
- 그리고 IVAF 로 tumor fraction 을 계산함.
IVAF = ( Sum of variant supporting reads ) / ( Sum of all reads at the clonal somatic mutations )
- 이 과정에서 sequencing error 에 대한 suppression 으로 random forest model 을 사용함
- 이 모델에서 error 를 포함하는 read, true variant 를 포함하는 read 를 사용하여 modeling 함.
- Fragmentation pattern, read sequence context 를 고려한 modeling ( cfDNA-specific )
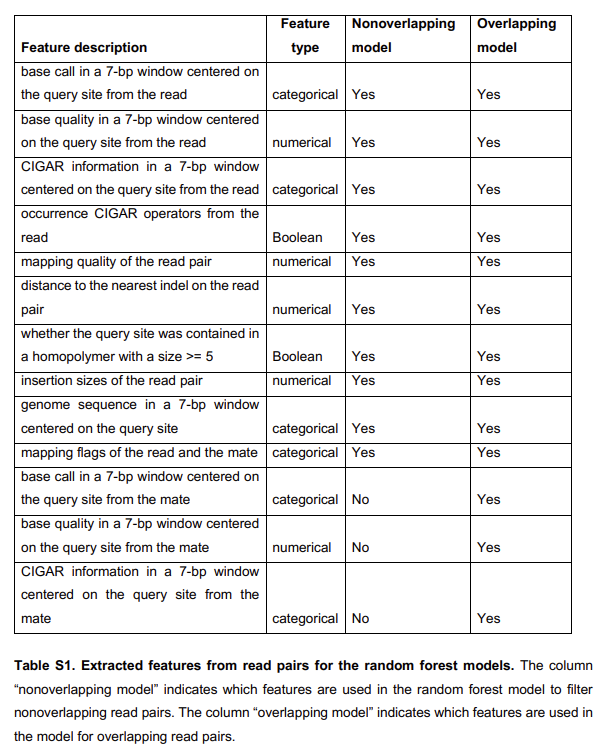
- Model 은 모든 supporting read 를 classify 하고, true variant 가 있는 read 만 variant supporting read 로 classify 함.
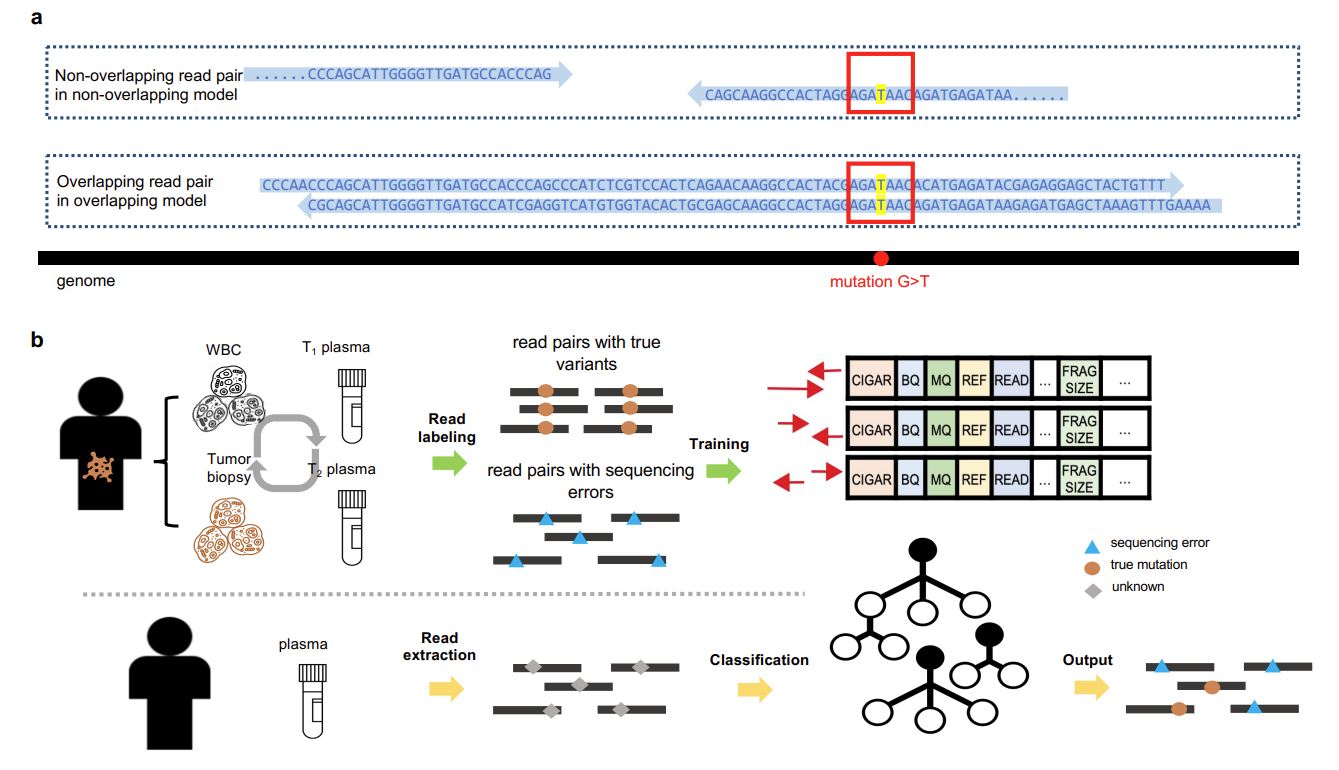
2) Post-treatment sampels
- Post-treatment sample 에서는 pre-existing, de novo mutation 둘 다 찾음.
3) MRD calling
- sample-specific background noise 분포 사용.
- PoN 의 background noise distribution 과 비교함.
- 이전 연구들에서는 post-treatment sample vs healthy sample 과의 비교를 진행했지만, 개인간 / 실험간 차이는 modeling 하기 쉽지 않음. 따라서 detection threshold를 일반화하기 어려움.
- 이에 각 샘플별로 따로따로 modeling 을 진행.
- n 개의 clonal tumor mutation 이 있다고 하면, genomic position 의 n개의 랜덤한 위치에서 100번 정도 반복적으로 IVAF 를 계산함. (알려진 mutation, CHIP 부위 제외 )
- 이론적으로 reference 와 다른 allele 을 가지고 있는 모든 read pair 는 sequencing error 로 부터 온 것이기 때문에, 이러한 read 들의 빈도는 background noise level 을 뜻함
 |
 |
| Figure from original paper | Figure from original paper |
- 이 distribution 에 기반하여 기존에 계산되어있던 tumor fraction ( IVAF ) 가 distribution 의 어디에 위치해있는지를 나타내는 empirical p value 를 사용해서 P<=0.05 이면 MRD call
4) de novo mutations
- cfSNV 사용
- cfSNV에서 나온 결과를 가지고, tumor fraction, 발견 된 mutation 의 개수를 input 으로 logistic regression modeling.
- cancer, healty sample 두개 합쳐서 training 하고 prediction score 가 healthy sample score 의 95% 이상이면 evolved tumor / newly emerged tumor 로 call 함.
Pretreatement sample 에서의 clonal mutation identification
- Tumor에서 유래된 somatic mutation : cfSNV
- 만약 pre-treatment sample 이 tumor sample 만 있을 때는 Strelka2, MuTect 로 call. WBC 에서 variant 가 존재하면 mutation 제외시킴 ( germline exclusion )
- 어떤 variant 의 VAF 가 한 샘플에서 가장 VAF 가 높은 5개 VAF 의 평균의 1/4 보다 크면 clonal variant 로 classify
- 분석에 들어가는 clonal variant 의 수는 30개 이상을 최소로 하고, 30개 이하려면 VAF 가 가장 높은 subclonal variant 도 포함시켜서 분석 진행
Mutation, CHIP 위치
- pre-treatment sample 에서의 germline mutation 은 strelka2 Germline, GATK haplotypecaller 를 사용해서 진행 ( WBC 이용 )
- Strelka2 는 plasma, WBC 둘 다 돌리고 haplotypecaller 는 pair mode 로 한번만 돌림
- 만약 변이가 없는 위치에서 3개 이상의 variant supporting read 가 있거나, WBC 상에서 VAF 1% 이상의 variant 가 있다면 CHIP 지역은 으로 말함
- 이렇게 정해진 mutation, CHIP, germline mutation 은 noise distribution 의 modeling 을 하는 데 있어서는 제외됨.
Sequencing error suppression
- Read-level error suppression
- 18명 , 각 환자는 4개의 샘플 채취
- sample 4개 : 2개 plasma ( 시점 다름 ) , WBC, tumor biopsy
- Known site, Error site 를 사용하여 modeling
- Known site 는 tumor-informed mutation ( Strelka, Mutect ) 를 포함
- Error site 는 4개 sample 중 오직 하나의 샘플에서만 150x 이상의 sufficient depth 를 가지면서 BQ>20, MQ>40 의 high-quality non-reference read 를 2개 이상 가지는 site 로 정의.
- picard tools FilterSamReads 로 high-quality read extraction
- mutation/error site 당 여러개의 read pair 가 존재할 수 있고, 이는 training/test dataset 상에서 redundancy problem 을 일으킬 수 있음. 따라서 site 당 하나의 read pair 만 가져가는 것으로 이를 해결
- Cross-validation 으로 model validation 진행. 18명 데이터 중 train : test 를 17:1 로, 즉 Leave-one-out 식으로 validation 진행함
- Independent dataset 으로 MBC, CRPC 환자로 test함
- Simulation 에 사용되는 샘플은 제외함
Simulation of MRD detection in pre-treatment sample
- cfTrack 을 시험해보기 위해서 MRD/recurrence 을 가지고 있는 환자 simulation data 생성함
- Post-treatment MRD (+) : Detection sensitivity 를 나타낼 것.
- Post-treatment MRD (-) : Detection specificity 를 나타낼 것.
- Sensitivity detection : in silico dilution. 50~200x
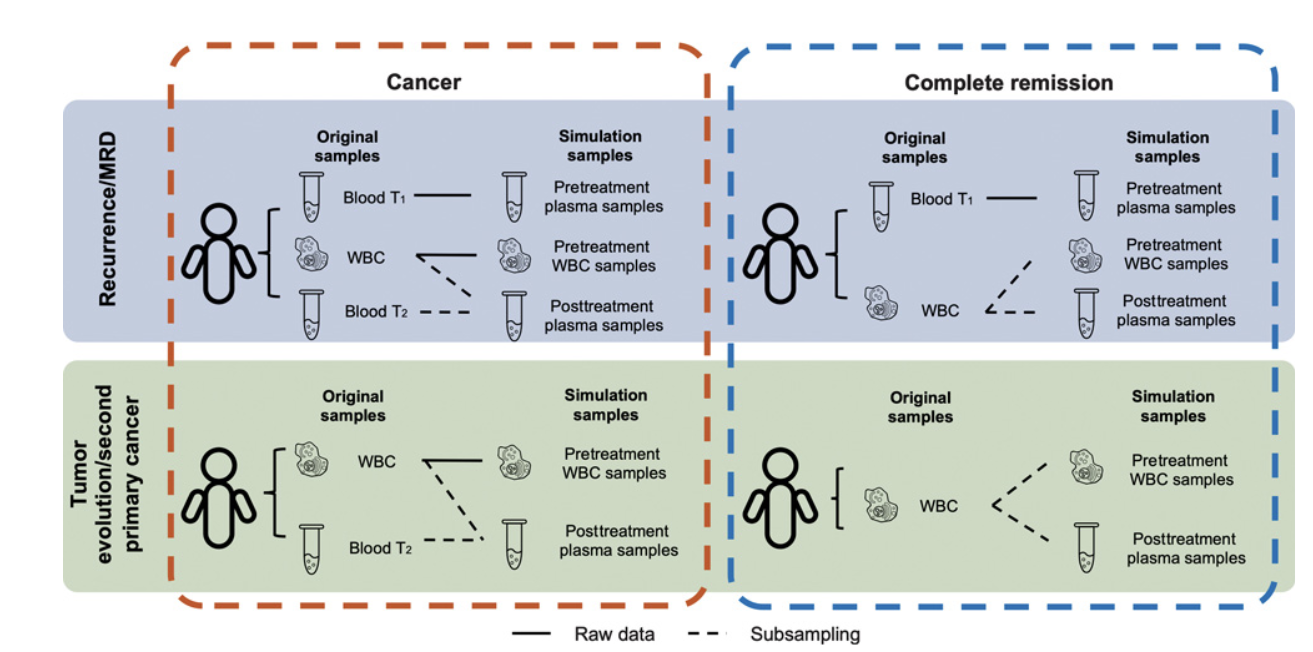
Simulation part 는 너무 복잡해서 나중에 다시 한번 정리...

댓글