Direct prediction of Homologous Recombination Deficiency from routine histology in ten different tumor types with attention-based Multiple Instance Learning: a development and validation study
Nadina Ortiz Bruechle, Jakob Nikolas Kather Groups
2023, medRxiv
Abstact
- Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD)는 PARP inhibitor 치료제 수혜를 받을 수 있는 환자군을 가리는 데 사용되 는 pan-cancer 바이오마커임.
- PARPi 치료제로 인한 DFS 개선은 많이 연구되었지만 HRD status 판단 여부가 어려움.
- 하미지만 HRD 는 매우 복잡한데, 이 논문에서 우리는 HRD status 를 염색된 H&E 조직 슬라이드로 예측하는 방법론을 탐구하였음.
- BRCA1/2 돌연변이가 HRD testing 에 제일 믿을만한 test인데 반해 non-BRCA HR mutation 은 불안정함. SBS3 가 잠재적인 후보가 될수도 있는데, 더 많은 바이오마커가 필요함.
- 논문에서는 attention-weighted multiple instance learning (attMIL) 방법론을 사용하였음.
- HRD score = loss of heterozygosity (LOH) + telomeric allelic imbalance (TAI) + large-scale state transitions (LST)
- HRD score 는 4,565 명의 두개의 독립 그룹의 WGS으로부터 구해짐
- 임상적으로 사용하는 수준의 HRD 예측치를 AUC의 statistical endpoint 로 정함
- Cross-validated AUROC 가 각각 endometrium, pancreas and lung 0.79, 0.58 and 0.66 이 나옴
- External cohort AUROCs of 0.93, 0.81 and 0.73
- Breast cancer data 로 training 된 HRD classifier 가 AUROC of 0.78 ( internal validation ) , 이것으로 endometrial, prostate and pancreatic cancer with AUROCs of 0.87, 0.84 and 0.67 결과 냄 : 여러 tumor 에서 HRD-like phenotype 이 공유됨을 시사
HRD score 계산
1. ASCAT 으로 구해진 SNP 데이터가 GDC 에서 다운로드됨
2. CPTAC 데이터는 CPTAC-3 cohort 에서만 사용가능했음
3. scarHRD 를 사용하여 HRD 를 계산했는데, 이는 LOH, LST, TAI 의 합임. 3 개의 점수의 cutoff 는 이전 출판된 것을 기준으로 했음.
4. 환자의 HRD group ( L,H ) 는 42 를 기준으로 나누어짐
모델

1. GDC Portal and TCIA 에서 WSI 다운로드
2. 이미지는 타일링됨 (with an edge length of 256 µm and a resolution of 224x224 pixel).
3. Macenko spectral matching technique 를 이용하여 각 코호트의 patch 가 color normalized 됨
4.self-supervised learning (SSL) model using a pre-trained ResNet50 인 In-house DL pipeline "marugoto" 를 이용하여 각 환자의 패치마다 2048-dimensional feature vector를 뽑아냄
5. 환자별로 512 개의 feature vector 가 랜덤하게 selection 되어서 512x2048 의 feature 매트릭스가 생성됨
6. 만들어진 feature 들은 attMIL framework with an architecture of (512x256), (256x2) 에 input 으로 쓰임
실험 디자인
1. 세 개의 메인 실험.
2. 5-fold CV 로 within-cohort valdiation 진행 (internal validation)
- 환자레벨로 각 코호트를 랜덤하게 나눔, 3:1:1 Training : validation : test
- 5개의 개별 모델을 훈련시킴. ( Training, test 절대 겹치지 않게 )
- TCGA 암종별로 이 작업을 반복
- 데이터 imbalance 를 위해서 weighted cross-entropy 사용
3. TCGA 로 학습한 데이터를 CPTAC 으로 validation ( external validation )
4. 가장 환자수가 많은 TCGA 유방암 샘플들에 대해서 HRD classifier 훈련시키고 CPTAC 으로 validation
- AUROC 신뢰구간 95% 로 모델 성능 결정
- HRD-H, HRD-L 그룹 간 prediction score 를 계산하여 correction 없이도 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나는지 검정 ( two-sided t test)
설명가능성

1. WSI 위에 heatmap 을 visualize
2.RetCCL 을 이용하여 convolutional neural network image feature vectors for 32x32 pixel fields were extracted from the WSIs.
3. Attention and classification scores 가 각 이미지 지역마다 계산되고, 각 환자의 코호트 안의 score 의 분포로부터 정규화됨.
3. Color heatmaps 이 각 환자별로 생성되고, 붉은색은 높은 attention, 파란색은 low attention 이나 negative classification 을 의미함 ( 잘못 분류된것 ?)
4. morphology에 설명가능성을 도입하기 위해, final attention 값과 classification 값을 raw image 위에 덧붙여봄.
5. 이 접근법은 예측된 값에 대해서 이해할 수 있게 해줌 ( 지역적으로 점수가 높은 곳이 실제로도 예측에 있어서 attention 이 많이 가해졌는가 ? )
-> 실제로 위의 figure 에서 attention 이 높은 곳은 classification score 가 높은 것을 볼 수 있음.
예측 결과 프로파일링
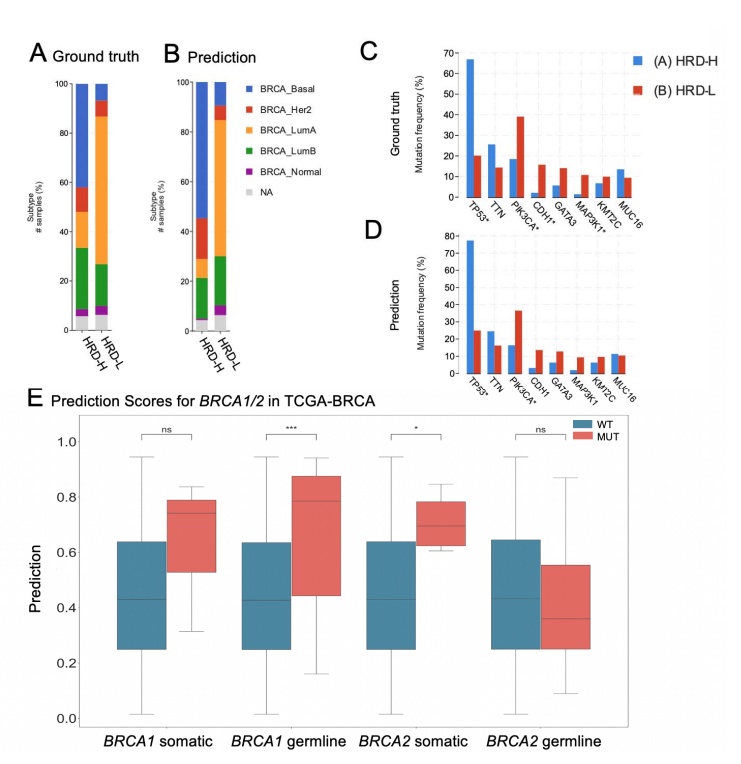
먼저 기존 ground truth 와의 비교를 진행함 (A~D) : 환자가 가지고 있는 molecular level 로 봤을 때 비슷하게 나타남을 알 수 있음

댓글